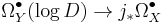Hyperhomology
In homological algebra, the hyperhomology or hypercohomology of a complex of objects of an abelian category is an extension of the usual homology of an object to complexes. It is a sort of cross between the derived functor cohomology of an object and the homology of a chain complex.
Hyperhomology is no longer used much: since about 1970 it has been largely replaced by the roughly equivalent concept of a derived functor between derived categories.
Contents |
Definition
We give the definition for hypercohomology as this is more common. As usual, hypercohomology and hyperhomology are essentially the same: one converts from one to the other by changing the direction of all arrows, replacing injective objects with projective ones, and so on.
Suppose that A is an abelian category with enough injectives and F a left exact functor to another abelian category B. If C is a complex of objects of A bounded on the left, the hypercohomology
- Hi(C)
of C (for an integer i) is calculated as follows:
- Take a quasi-isomorphism Φ : C → I, here I is a complex of injective elements of A.
- The hypercohomology Hi(C) of C is then the cohomology Hi(F(I)) of the complex F(I).
The hypercohomology of C is independent of the choice of the quasi-isomorphism, up to unique isomorphisms.
The hypercohomology can also be defined using derived categories: the hypercohomology of C is just the cohomology of F(C) considered as an element of the derived category of B.
The hypercohomology spectral sequences
There are two hypercohomology spectral sequences; one with E2 term
- Hi(RjF(C))
and the other with E1 term
- RjF(Ci)
and E2 term
- RjF(Hi(C))
both converging to the hypercohomology
- Hi+j(C),
where RjF is a right derived functor of F.
Examples
- For a variety X over a field k, the second spectral sequence from above gives the Hodge to de Rham spectral sequence for algebraic de Rham cohomology:
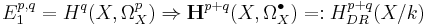
- Another example comes from the holomorphic log complex on a complex manifold. Let X be a complex algebraic manifold and
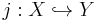 a good compactification. This means that Y is a compact algebraic manifold and
a good compactification. This means that Y is a compact algebraic manifold and 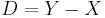 is a divisor on
is a divisor on 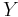 with simple normal crossings. The natural inclusion of complexes of sheaves
with simple normal crossings. The natural inclusion of complexes of sheaves
turns out to be a quasi-isomorphism and induces an isomorphism
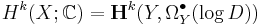 .
.
See also
References
- H. Cartan, S. Eilenberg, Homological algebra ISBN 0691049912
- V.I. Danilov (2001), "Hyperhomology functor", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=H/h048480
- A. Grothendieck, Sur quelques points d'algèbre homologique Tohoku Math. J. 9 (1957) pp. 119-221